China Achieves Historic Satellite Refueling
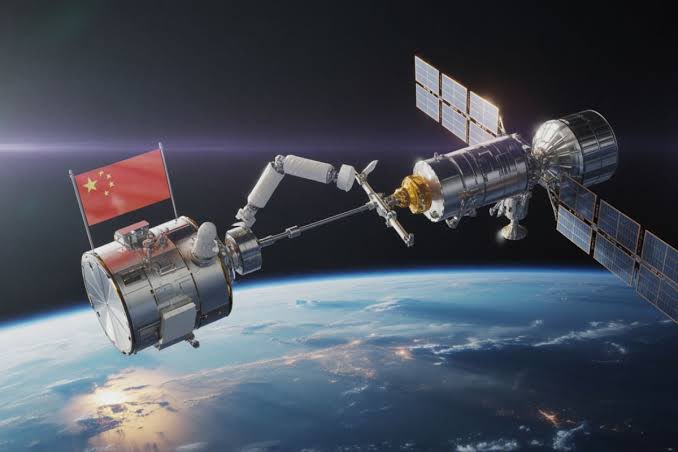
China has reportedly become the first nation to successfully perform China satellite refueling in orbit. This historic achievement could redefine the future of space operations. International space tracking companies observed the mission, which demonstrates a sophisticated level of in-space logistics and technology. Such a capability has long been a goal for space agencies worldwide.
The mission used two of China’s Shijian satellites, SJ-21 and SJ-25. They performed a complex docking maneuver in geostationary orbit (GEO), about 22,000 miles (35,786 kilometers) above Earth. Chinese officials have not yet confirmed the details. However, data from independent providers like COMSPOC and S2A Systems shows the two satellites docked for several days in early July 2025.
The Technical Feat of In-Orbit Satellite Refueling
In-orbit refueling is a difficult and high-stakes operation. It requires a series of precise, autonomous maneuvers. The spacecraft must rendezvous, dock, and transfer fuel in the vacuum of space. The challenge is greater in geostationary orbit. Satellites there must maintain a constant speed, which makes intricate movements complex.
The newer SJ-25 approached and docked with the older SJ-21. China launched the SJ-25 in January 2025 to test satellite refueling technology. The SJ-21 was an ideal test candidate. It had used most of its fuel in a previous mission, towing a defunct satellite to a “graveyard” orbit in 2022. This capability to autonomously perform such a delicate procedure at high altitude is a major technological leap.
DARPA’s Orbital Express mission demonstrated similar concepts in 2007, but in low Earth orbit. China’s success in the more challenging GEO environment puts it at the forefront of this critical technology.
The Strategic and Economic Implications
The successful refueling operation has far-reaching implications for the commercial space industry and global security.
- Extended Satellite Lifespans: A satellite’s fuel supply currently limits its lifespan. Refueling satellites keeps valuable, multi-million dollar assets in service for years longer. This reduces the need for expensive and frequent launches.
- Reduced Space Debris: A refueled satellite can continue its mission instead of becoming space debris. This helps mitigate the growing problem of orbital congestion.
- A “Dual-Use” Technology: International analysts are discussing the military and strategic applications of this technology. The same capabilities used for peaceful refueling can also be used for other purposes, such as inspecting or even interfering with other nations’ satellites. This “dual-use” nature of the technology has concerned the U.S. and other countries, highlighting a new dimension to the ongoing space race.
The Road Ahead
This achievement underscores China’s rapidly growing prowess in space technology and its ambitious long-term goals. With this successful demonstration, China is enhancing its space infrastructure and setting a new standard for in-space services. The world will now watch for official confirmation and for the next steps in this new era of on-orbit servicing and logistics.












Post Comment