How Blockchain Technology Works: A Simple Explanation for Everyone
Ever heard of blockchain and felt a little lost? You’re not alone! It certainly sounds complex, but at its heart, blockchain is a surprisingly straightforward idea. Essentially, think of it like a digital, unchangeable record book that’s shared across many computers. Consequently, instead of one person holding all the records, everyone has a copy, making it incredibly secure and transparent.
The “Blocks”: Pieces of Information
Imagine you’re writing down a list of transactions – who sent money to whom, when, and how much. In a blockchain, however, these transactions are grouped together into a “block.” Specifically, each block contains:
- Transaction Data: Details of all the recent transactions (e.g., “Alice sent 1 Bitcoin to Bob,” “Charlie bought an NFT”).
- A Timestamp: This indicates when the block was created.
- A Cryptographic Hash: Think of this as a unique digital fingerprint for the block. Moreover, it’s a complex code generated from all the data within that specific block. Even a tiny change to the data, therefore, would completely change the hash.
- The Hash of the Previous Block: This element proves crucial! Indeed, each new block always includes the digital fingerprint (hash) of the block that came before it. Ultimately, this is what creates the “chain.”
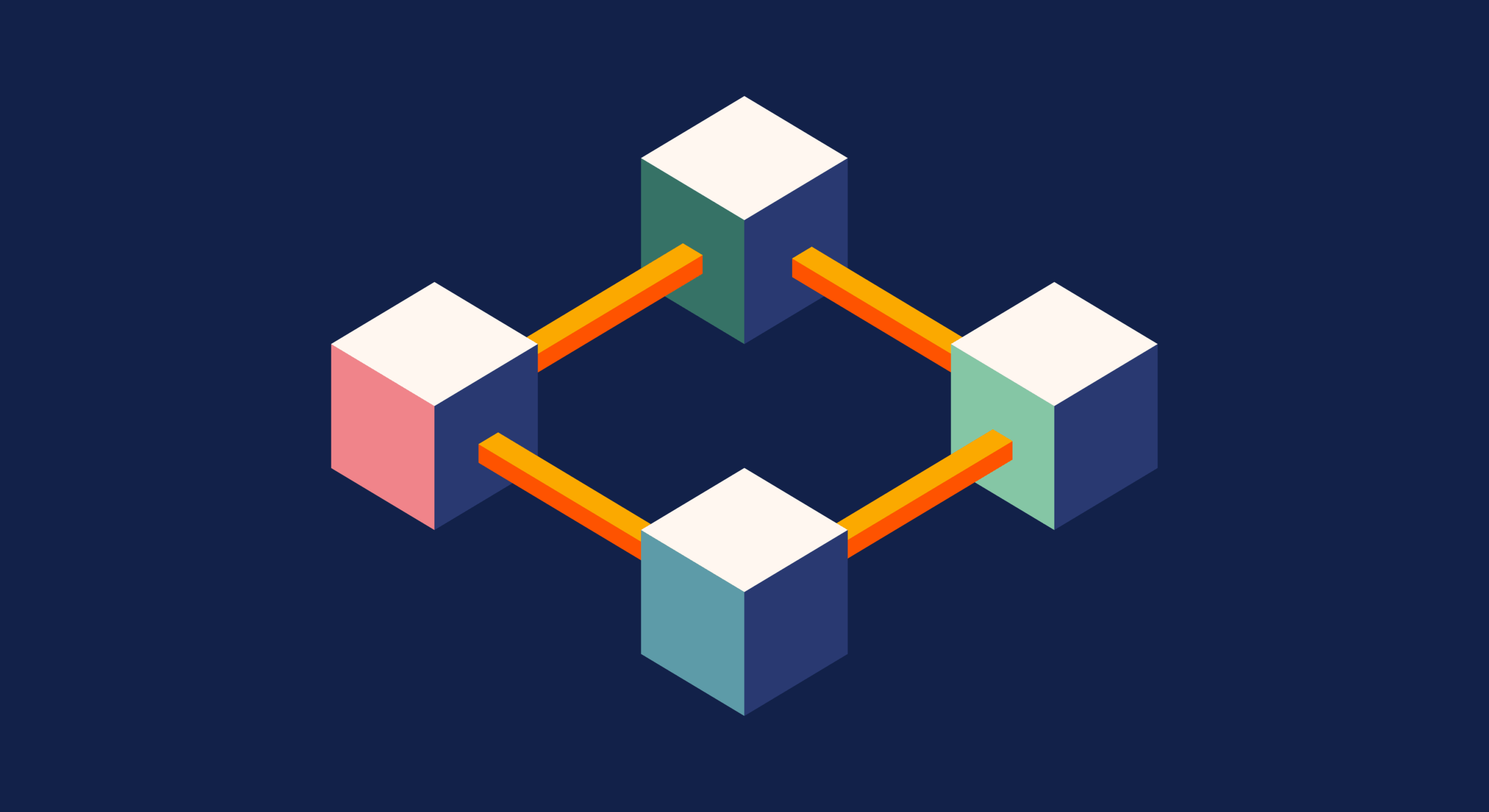
The “Chain”: Linking Blocks Together
Once a block is filled with transactions, it’s sealed and then connected to the previous block using its hash. As a result, this process creates a “chain” of blocks, which continually grows longer over time. Because each block explicitly contains the hash of the one before it, if someone tries to tamper with an old block, its hash would immediately change. Consequently, that change would break the vital link in the chain. Consider it like trying to remove a page from a physical ledger where every page is glued to the next with a unique, tamper-proof seal.
The “Network”: Shared and Secure
Furthermore, this digital ledger isn’t stored in one central place. Instead, thousands of computers (called “nodes”) around the world all have a copy of the entire blockchain. Therefore, when a new block is created and verified, it is added to everyone’s copy of the chain.
This distributed nature proves key to its security:
- Verification: Before a new block is added, the network of computers actively verifies all the transactions within it. They check if the sender has enough funds, if the signatures are correct, and so on.
- Consensus: For a new block to be accepted, the majority of the computers on the network must agree that the block and its transactions are valid. This “agreement” process is called consensus. Different blockchains use various methods for consensus; for instance, Proof of Work (PoW) is used by Bitcoin, while Proof of Stake (PoS) is utilized by Ethereum.
- Immutability: Once a block is added to the chain and accepted by the network, changing or deleting it becomes practically impossible. This is because every subsequent block contains its hash. Hence, altering an old block would mean changing all the blocks that came after it – a task that would require immense computing power and agreement from the entire network, which is virtually impossible.
Why Is Blockchain So Revolutionary?
The combination of blocks, chains, and a distributed network consequently creates a system with several powerful characteristics:
- Decentralization: No single entity controls the blockchain. This means there’s no single point of failure and less vulnerability to censorship or manipulation.
- Transparency: All transactions on a public blockchain are visible to everyone on the network. However, while identities might be pseudonymous (using wallet addresses instead of names), the transaction data itself remains open.
- Security: The cryptographic linking of blocks and the distributed nature of the network make hacking or tampering with the data incredibly difficult.
- Immutability: Records, once added, are permanent and cannot be altered. This, in turn, creates a trustworthy and verifiable history.
- Efficiency: For certain applications, blockchain can streamline processes by removing the need for intermediaries and speeding up verification.
Beyond Bitcoin: What Else Can Blockchain Do?
While blockchain technology first gained fame as the backbone of Bitcoin, its potential extends far beyond just cryptocurrencies. It’s currently being explored and actively used in various fields:
- Supply Chain Management: Tracking goods from origin to consumer to ensure authenticity and prevent fraud.
- Voting Systems: Creating more transparent and secure elections.
- Healthcare: Managing patient records securely and ensuring data privacy.
- Intellectual Property: Proving ownership and timestamping creations like art or music (think NFTs!).
- Digital Identity: Creating secure, self-sovereign digital identities that individuals control.
In essence, blockchain technology provides a way to create a secure, transparent, and tamper-proof record of anything digital. Ultimately, it is a foundational innovation that’s paving the way for a more decentralized and trustworthy digital future.











Post Comment